“Do STDS go away?”
“Most STDs are preventable, manageable and curable, but a few are incurable, such as AIDS.”
What if I have an STD?
1. Don’t panic, go to the hospital!
Don’t be shy about being treated, and go to a regular medical institution to receive standardized diagnosis and treatment in time.
2. Don’t be afraid, there is no shame in seeing a doctor!
Do not go to illegal medical institutions or seek medical treatment, do not buy your own medicine treatment.

3. Don’t stop, just do whatever the doctor says!
Venereal disease patients should follow the doctor’s advice treatment, during the period do not stop at will, change the type of drugs or increase or decrease the dose of drugs, to avoid drug resistance, delay the condition.
4. Don’t worry, thorough treatment is very important!
After treatment, we should review and follow up as required to observe the effect of treatment, reduce the occurrence of complications and sequelae, and restore health as soon as possible.
What is the STDs?
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDS) are a group of infectious diseases that are mainly transmitted through sexual contact. At present, China’s key prevention and control of STDs are syphilis, AIDS, gonorrhea, condyloma acuminatum, genital herpes and genital chlamydia trachomatis infection. STDs are mainly sexual behavior, but also may be transmitted through blood, mother and child, contaminated living utensils.
Most STDS are preventable, controllable and treatable, and only a few are incurable, such as AIDS.
Venereal disease is widespread and is one of the most prevalent infectious diseases in our country. In recent ten years, the incidence of VENEREal disease on the whole has been increasing year by year, and the infection rate is relatively high among prostitution and whoring, multiple partners, and male homosexual behavior, which has become an important public health problem and social problem.

How do venereal diseases spread?
STDs are mainly transmitted through sexual transmission, but also through mother and child, blood transmission. For example, syphilis can infect the fetus through the placenta.
In rare cases, STDS can be transmitted through close contact or contaminated household utensils.
What are the risks of STDS?
Venereal disease damage to human health is many aspects, infection after venereal disease can not be found and standardized treatment in time, not only damage reproductive organs lead to infertility, but also to the fetus or newborn, some venereal disease can also cause damage to multiple organs of the human body, such as cardiovascular, nerve, bone, etc., resulting in disability and even death.
What are the common venereal diseases in clinic?
Syphilis
Syphilis is a chronic, systemic sexually transmitted disease caused by spirochaeta pallidum (syphilis).
Early symptoms are sores or rashes on the mucous membranes of the skin in the genital area or other sexual contact sites, which are not painful or itchy and are easy to ignore.
Many people have no symptoms after infection with syphilis, called “latent syphilis”. This condition is still dangerous to the human body, and it is also somewhat contagious.
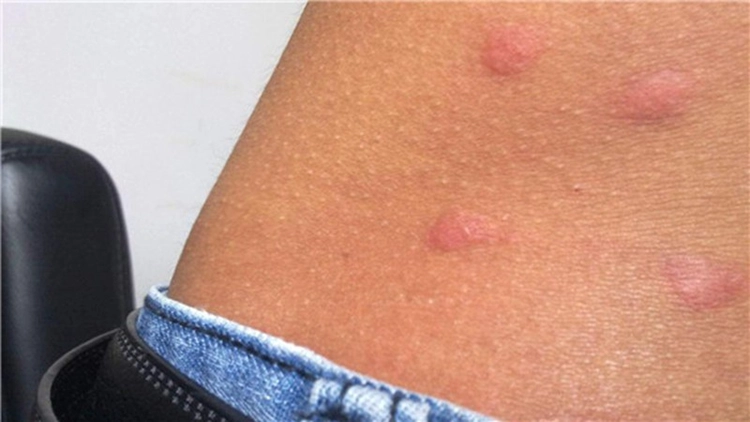
Primary syphilis: Usually develops about 2 to 3 weeks after infection, and mainly presents as a chancre and swollen lymph nodes. Chancre initially presents as a small erythema of the external genitalia, which becomes necrotic and forms a round or oval painless ulcer with a diameter of 1-2cm. It is highly contagious. 1 to 2 weeks after the appearance of the chancre, the lymph nodes in the groin or near the affected area may be significantly enlarged, but without pain.
Secondary syphilis: 3 to 4 weeks after resolution of the hard chancre (9 to 12 weeks after infection), it may appear in conjunction with the hard chancre. Syphilid can cover the skin and mucous membranes all over the body, even the palms and soles of the feet, and can appear as red or reddish-brown papules, maculopapules, plaques, etc., usually without obvious itching. The rash usually resolves within 2 to 3 months, and syphilis is highly contagious during this stage.
Tertiary syphilis: Untreated or inadequately treated primary and secondary syphilis can occur in 40% of patients after 3-4 years (2 years at the earliest, 20 years at the latest). This stage of weak infectivity, in addition to the skin mucosa, can also occur skeletal syphilis, cardiovascular syphilis, neurosyphilis.
Treatment
Penicillin is the treatment of choice for syphilis. Sometimes after formal treatment, non-specific antibodies still have weak positive (1:2 or 1:4), has not been able to become negative, we call serum fixation, if 3 months, 6 months, 1 year review titer did not rise on the need for treatment. Syphilis can be cured after early detection and timely treatment. It is recommended to go to the hospital in time when infection is suspected.
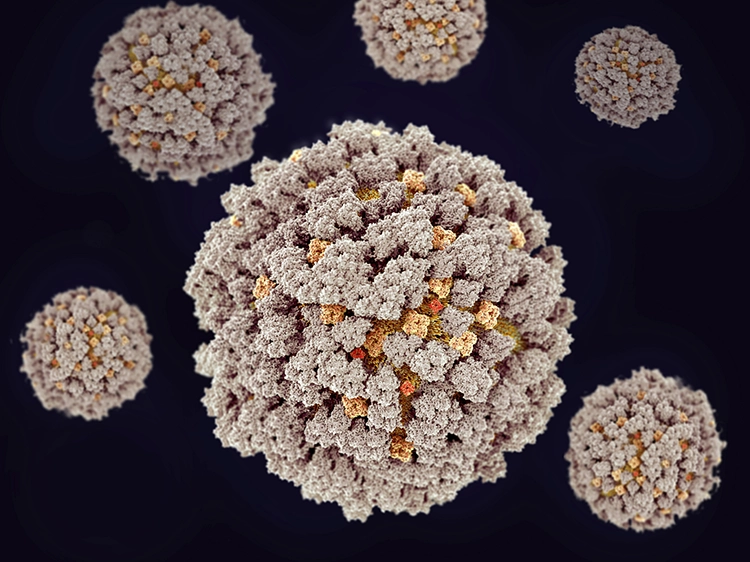
Condyloma acuminatum
Caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
A cutaneous mucous growth, often in the anus and external genitals
It can be treated with laser, cryotherapy, and photodynamic therapy
HPV infection has an incubation period and is prone to recurrence
Condyloma acuminatum is a sexually transmitted disease caused mainly by warty lesions caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The disease is highly infectious, easy to relapse, and requires a long time of repeated treatment, which seriously affects the daily life of patients.
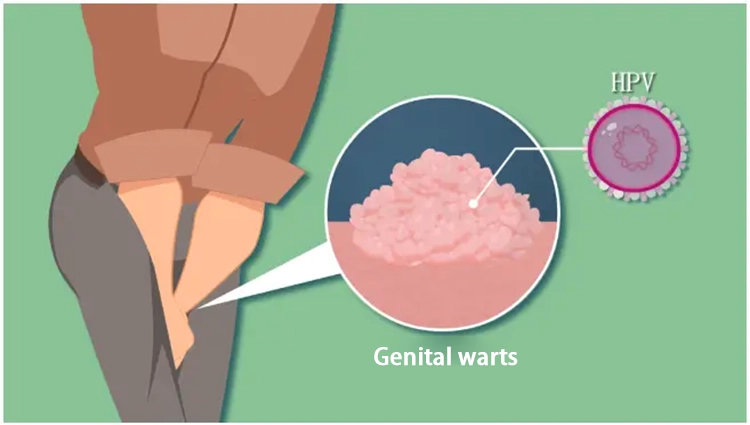
Clinical manifestations: The initial manifestations of skin lesions are local small papules, the size of the needle to mung bean, gradually increasing or increasing, spreading around, spreading, and gradually developing into papillary, cockscomb, cauliflower or clumpy neoplasms. The lesions may occur singly or multiple. The color can range from pink to dark red (non-keratosis), gray (severe keratosis) or even brownish black (pigmented lesions). A small number of patients due to immune dysfunction or pregnancy and large volume of warts, can involve the whole vulva, anal and hip groove, called giant condyloma acuminatum.
Patients generally have no conscious symptoms, a small number of patients can feel itching, foreign body sensation, pressure or burning sensation, can be due to brittle increase in skin, friction and rupture, impregnation, erosion, bleeding or secondary infection. Female patients can have increased vaginal secretions.
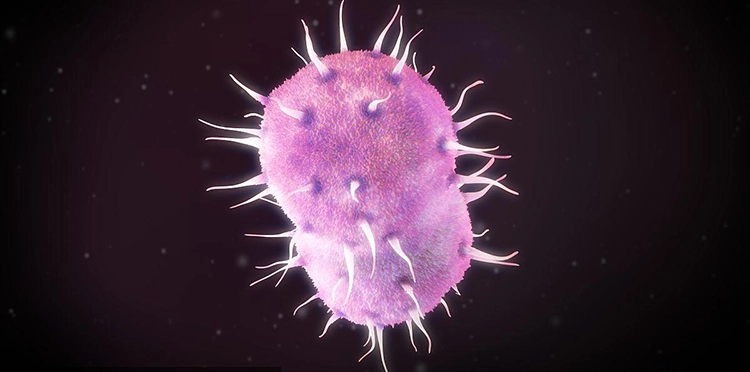
Gonorrhea
A suppurative infection of the genitourinary system caused by infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
It mainly presents with purulent discharge from the urethral orifice in men and purulent discharge from the vaginal orifice in women.
It occurs in sexually active people.
It is mainly treated with antibiotic drugs.
Gonorrhea transmission ability is very strong, ranking the fourth class B infectious diseases in China. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcus gonorrhoeae for short) with purulent infection of urogenital system as the main manifestation.

It is manifested as urethritis in men and cervicitis and urethritis in women.
The main symptoms include frequent urination, urgent urination, urinalgia, discharge of pus from the urethral orifice or purulent secretions from the cervix or vaginal orifice.
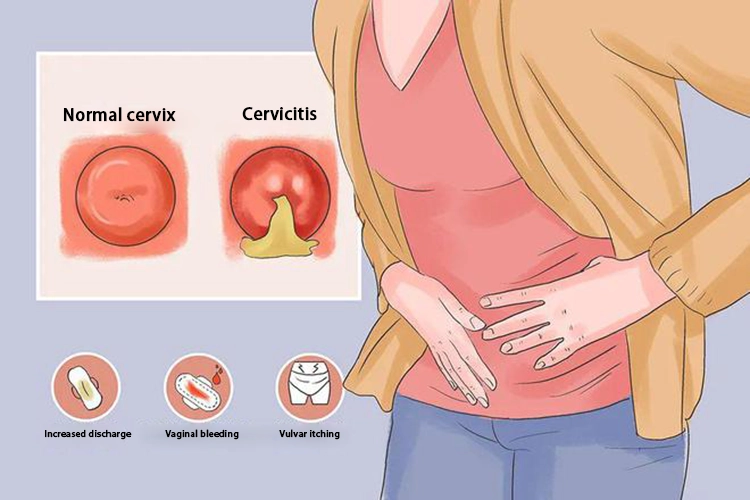
Women often have asymptomatic infections.
People who often have multiple sexual partners, or people who have been exposed to risk factors such as gonorrhea infection history, found that the urethra or vagina has mucoid or purulent discharge, urethra irritation pain and other symptoms, should be timely to the dermatology and venereal disease department and other departments.

Genital herpes
A sexually transmitted disease caused by infection with the herpes simplex virus.
It occurs in sexually active men and women between the ages of 15 and 45.
It presents as blisters, burning, and pain in the genital area.
Antiviral drug treatment is the main, resistance is easy to relapse when the decline.
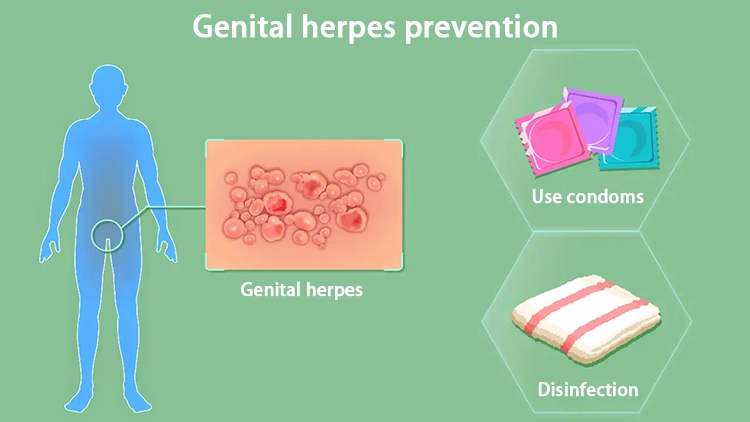
Genital herpes is caused by infection with herpes simplex virus (HSV).
Genital herpes is clinically manifested as single or clusters of blisters on the genitals, perineum, perianal area, buttocks, or upper thighs that develop ulcers before subsiding.
The clinical presentation of genital herpes is often atypical with asymptomatic viral shedding, which poses a great challenge for clinical management.
AIDS
HIV is a virus that lives in a person’s blood and primarily targets CD4+T lymphocytes. HIV itself does not cause disease, but death from a variety of clinical symptoms and diseases that occur when an infected person’s immune system is destroyed by HIV.
Acute Phase
Symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection, such as fever, fatigue, sore throat and general discomfort, usually occur 1 to 2 weeks after exposure to HIV; Some patients have headache, rash, meningoencephalitis or acute polyneuritis; Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, axillary, and occipital regions, similar to infectious mononucleosis or hepatosplenomegaly.
Asymptomatic phase
There are usually no obvious symptoms and signs, and some patients may have persistent lymph node enlargement and maintain for a considerable time.
AIDS stage
Unexplained immune dysfunction; Persistent irregular low fever for more than 1 month; Persistent, unexplained, generalized lymph node enlargement (lymph nodes greater than 1cm in diameter); Chronic diarrhea more than 4 to 5 times per day and weight loss greater than 10% within 3 months; Combined with oral candida infection, pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, cytomegalovirus infection, toxoplasmosis, cryptococcal meningitis, rapid progression of active tuberculosis, lymphoma, etc.; Dementia occurs in young and middle-aged patients.
At present, there is still a lack of effective drugs to cure HIV infection worldwide. After the occurrence of high-risk behaviors, it is recommended to start prophylactic treatment as early as possible, with antiretroviral drugs taken within 72 hours at the latest for 28 days to deal with the possibility of infection from potential exposure. Testing is also recommended at one to three months after exposure.

Be careful! These STDS, even condoms won’t protect against them
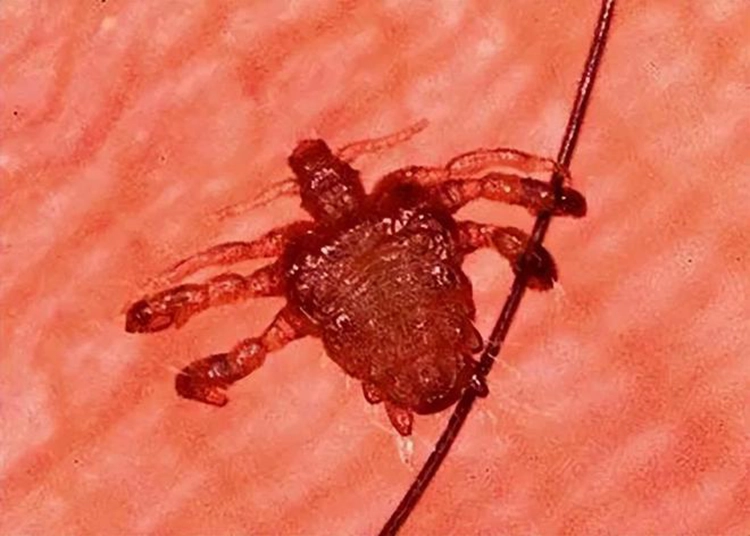

1. Pubic lice
During sex, pubic lice can be transmitted directly through pubic hair, because the safety sleeve does not reach the pubic hair, so there is no way to stop the “footsteps” of pubic lice, and importantly, even if you do not have sex, you can also be infected. For example: sharing a bath towel with the patient, touching the patient’s body hair or clothing, sitting on the patient’s bed, etc.

2. Syphilis
It can be spread in a wide way, not only through blood transmission, but also in many places that condoms can’t cover, such as kissing, if there is a small wound in the mouth, you may be infected, which is really “difficult to talk about” ah.

3. Gonorrhea
Condoms don’t protect against gonorrhea, mainly because of the infection virus, gonococcus. It likes to cling to wet things and can live for a day or two. This means that if you share toiletries or the same toilet with someone who has it, you could get infected!

How to prevent STDS?
Clean self love, avoid sexual disorderly behavior, put an end to unsafe sex;
When having sex, use condoms correctly throughout (quality to be qualified);
Actively participate in premarital, prenatal STD screening, once found infection should be treated as early as possible;
People who have unsafe sex such as multiple sex partners and frequent changes of sex partners should regularly go to the hospital for examination;
After the diagnosis of STDs, sexual partners should be promptly notified to the hospital for examination, if found to be infected with timely treatment.

